The chemical distribution and manufacturing industry is embracing circular economy principles, aiming to eliminate waste and extend product lifecycles. Innovations like closed loop extraction systems and universal recycling technologies are leading this sustainable transformation.
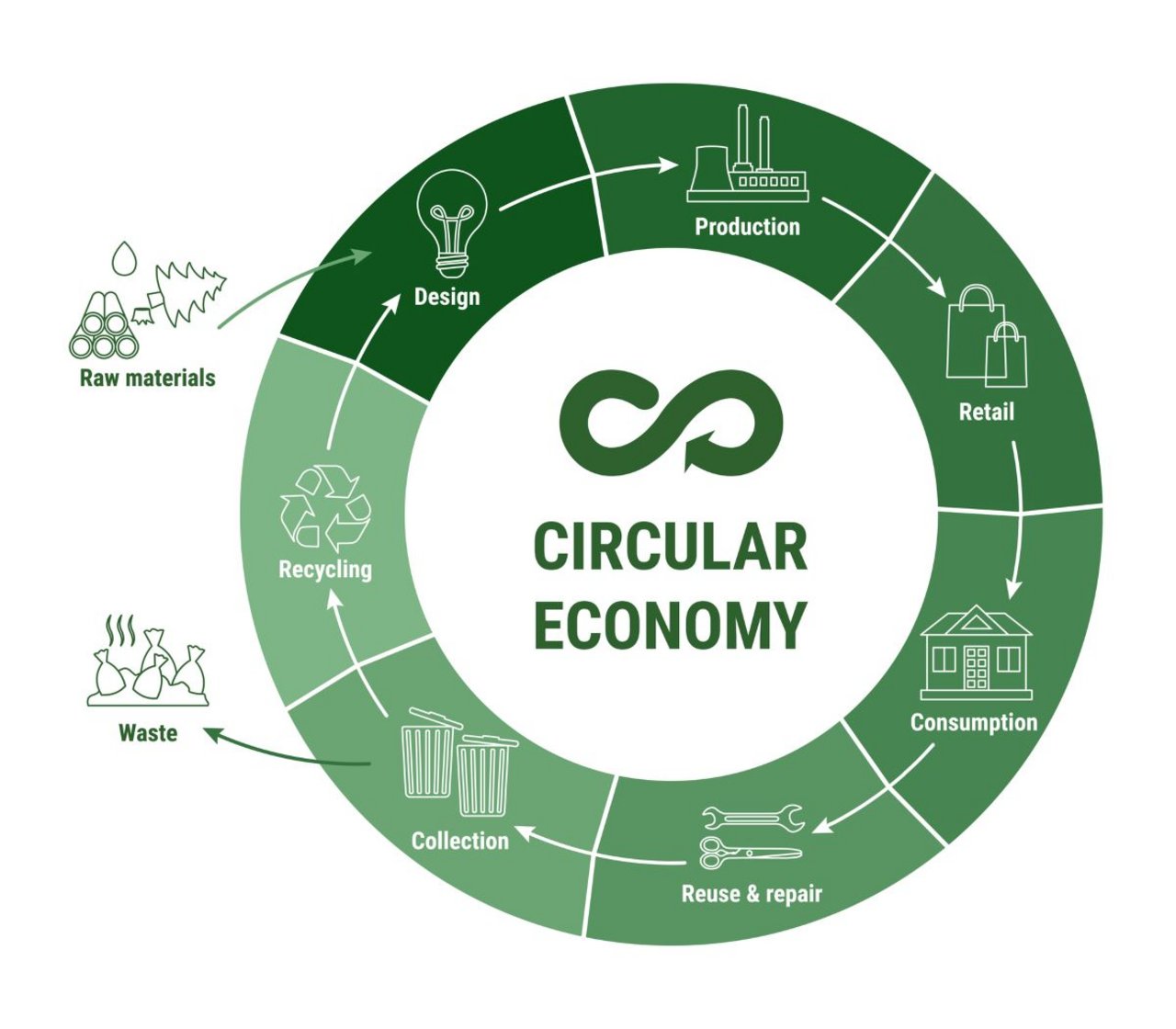
The chemical distribution and manufacturing industry is undergoing a significant transformation, spearheaded by the circular economy principles. As industries worldwide grapple with environmental concerns, the shift from a linear to a circular economy action plan and model is not just a trend but a necessity. This paradigm shift focuses on eliminating waste, maintaining the use of products and materials, and regenerating natural systems, ultimately aiming for sustainable growth and reduced environmental impact.
One of the hottest topics regarding the circular economy action plan is the implementation of closed loop extraction systems. In traditional linear economies, products are made, used, and discarded. However, in a circular economy, end-of-life products are reintegrated into the production cycle, minimizing waste and resource extraction. This concept is particularly relevant in chemical manufacturing, where raw materials can often be repurposed and reused, reducing the need for virgin resources and decreasing environmental footprints.
The benefits of closed loop extraction systems extend beyond environmental impact. Economically, these systems can reduce costs associated with raw material procurement and waste management. By continuously recycling chemical materials within the production process, companies can stabilize supply chains and mitigate risks related to resource scarcity. Furthermore, closed loop extraction systems encourage innovation in product design, prompting manufacturers to create more durable, repairable, and upgradable products.

Recycling and reuse are cornerstones of the circular economy action plan. In the chemical industry, universal recycling technologies are being developed to break down complex polymers and other materials into their original monomers, which can then be reused to create new products. This not only reduces waste but also decreases the demand for new raw materials, leading to significant energy savings and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Universal recycling technologies such as chemical recycling, pyrolysis, and gasification are transforming how the industry handles waste. Chemical recycling, for instance, allows for the decomposition of plastics into their molecular building blocks, which can then be repurposed into new chemicals or fuels. This method is particularly effective for dealing with plastic waste that is difficult to process through traditional mechanical chemical recycling. Pyrolysis and gasification convert organic waste into syngas and bio-oil, which can be used as energy sources or as feedstock for new chemical products.
In addition to these methods, advancements in universal recycling technologies are expanding the possibilities for sustainable waste management. These technologies are being continually refined to handle a wider variety of materials for chemical recycling, further supporting the circular economy.
Another critical aspect is the design of products for longevity and easy disassembly. Chemical distribution and manufacturing companies are innovating to create products that are easier to recycle at the end of their life cycle. By designing for disassembly, components can be efficiently separated and reused, further supporting the circular model. This approach requires a shift in mindset from designing for the end product to designing for the entire lifecycle of the product.
Designing for longevity involves selecting durable materials and creating modular products that can be easily repaired or upgraded. This reduces the frequency of replacements and extends the useful life of products. Moreover, designing for disassembly involves creating products that can be taken apart with minimal damage, ensuring that valuable materials and components can be recovered and reused. This practice not only supports sustainability but also opens new business opportunities in the areas of repair and refurbishment.

Digitalization and data analytics can significantly enhance the efficiency of chemical distribution networks by optimizing routes and reducing waste, and also play a pivotal role in advancing the circular economy action plan. With the advent of Industry 4.0, chemical distribution companies and manufacturers can leverage big data and the Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize resource use, improve process efficiencies, and enhance supply chain transparency. Real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance can reduce waste, prevent downtime, and extend the life of equipment and materials.
Data analytics can provide insights into material flows and product life cycles, enabling chemical distribution and manufacturing companies to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. IoT devices can monitor the condition of equipment and products in real-time, predicting failures before they occur and scheduling maintenance proactively. Additionally, digital platforms can facilitate the tracking and tracing of materials throughout their life cycles, ensuring that they are reused or recycled at the end of their use.

Industrial symbiosis is another powerful strategy within the circular economy action plan, where different industries collaborate to use each other's by-products and waste streams as resources. In the chemical distribution industry, this could involve using waste heat from one process to power another or using waste chemicals as raw materials for different production lines. This approach not only reduces waste but also enhances resource efficiency and lowers overall production costs.
For instance, a chemical plant could supply its waste heat to a neighboring facility that requires thermal energy, reducing the latter's need for external energy sources. Similarly, a company producing bio-based chemicals might use agricultural waste as a feedstock, turning what would otherwise be a disposal problem into a valuable resource. Such symbiotic relationships can significantly enhance the sustainability of industrial operations and create economic benefits for all parties involved.
The transition to a circular economy action plan in the chemical distribution and manufacturing industry is complex, but it is essential for achieving long-term sustainability. It requires a concerted effort from all industry players to rethink traditional practices and embrace innovative solutions. Governments and regulatory bodies also play a crucial role by providing the necessary support through policies and incentives that encourage circular economy principles and practices.
Regulations that mandate chemical recycling and waste reduction, coupled with incentives for using recycled materials, can accelerate the adoption of circular economy principles in both the chemical distribution and manufacturing industries. Policies that promote research and development in sustainable technologies, as well as those that facilitate industrial symbiosis, can further drive the industry towards a circular economy model. Moreover, international cooperation and harmonization of standards can ensure that circular practices are implemented consistently across borders, enhancing their overall impact.

Education and collaboration are vital to the successful implementation of the circular economy action plan in the chemical distribution and manufacturing industry. Industry stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, and customers, need to be educated about the benefits and practices of the circular economy. Collaborative efforts between companies, research institutions, and government agencies can foster innovation and share best practices, driving the industry towards a more sustainable future.
Educational initiatives can include workshops, seminars, and training programs that highlight the importance of sustainability and the practical steps that can be taken to achieve it. Collaborative platforms can facilitate the exchange of knowledge and resources, enabling companies to learn from each other's experiences and adopt successful strategies. By working together, the chemical distribution and manufacturing industry can overcome the challenges of transitioning to a circular economy action plan and make significant strides towards sustainability.

Innovation is at the heart of the circular economy action plan. The development of new materials, processes, and universal recycling technologies that support sustainability is crucial for the chemical distribution and manufacturing industry. Innovations such as biodegradable plastics, sustainable chemical processes, and universal recycling technologies are paving the way for a more circular and sustainable industry.
Research and development efforts are essential for discovering new materials that are easier to recycle and have lower environmental impacts. Innovations in process engineering can improve the efficiency of chemical reactions and reduce waste. Furthermore, advancements in universal recycling technologies can expand the types of materials that can be effectively recycled, reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.

HSH Chemie, the No. 1 chemical distributor in Central and Eastern Europe, is committed to integrating circular economy principles into its operations. As a member of the European Association of Chemical Distributors (Fecc), representing around 1,600 companies, we actively contribute to shaping industry standards and policies. We are proud to be a part of the Fecc's Circular Economy Committee, which plays a crucial role in developing policy papers that will guide the European Union's approach to the circular economy action plan. Our involvement ensures that we are not only adhering to the highest standards but also influencing them.
The committee's mission includes implementing circularity in business and production processes, facilitating compliance guidance for SMEs, exchanging best practices, and supporting umbrella initiatives for piloting innovative circular economy principles and solutions. These efforts aim to embed sustainable practices into the chemical distribution industry and foster collaboration and innovation.
Through our involvement in the Fecc, HSH Chemie focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency within our supply chain. By participating in industry forums and working with regulatory bodies, we promote the benefits of a circular economy action plan and encourage broader adoption of sustainable practices.
The circular economy action plan represents a critical shift for the chemical distribution and manufacturing industry. By embracing closed loop extraction systems, universal recycling technologies, chemical recycling, product design for longevity, and digitalization, the industry can significantly reduce its environmental impact. However, the journey towards a fully circular economy is ongoing and requires continuous innovation, collaboration, and commitment from all stakeholders.
The future of the circular economy action plan in the chemical distribution and manufacturing industry is promising, with many companies already making significant progress. As more organizations adopt circular economy principles and practices such as chemical recycling and closed loop extraction systems, the industry will move closer to achieving its sustainability goals. The combined efforts of manufacturers, policymakers, researchers, and consumers will drive the transformation towards a more sustainable and resilient chemical distribution and manufacturing industry.
In conclusion, the transition to a circular economy action plan in the chemical distribution and manufacturing industry is not just a necessity but an opportunity to create a more sustainable future. By rethinking traditional practices and embracing innovative solutions, the industry can reduce its environmental impact, enhance resource efficiency, and contribute to global sustainability efforts. Together, we can build a future where resources are used efficiently, waste is minimized, chemicals are recycled, and the environment is protected for generations to come.
Interested in reading more of our industry news? Check out our last article on The Importance of Natural Antipollution Agents in Make-Up.
Is there anything we can do for you? If you are interested in our sustainable products or need more information,
please let us know! Use our contact form to get in touch with our expert team.